Table Of Content

1, as a ring-like scattering intensity at q-values of ∼0.1 Å-1 and a broad, ring-like scattering at ∼1.5 Å-1 as a result of the lipid order within the membrane layers. The corresponding diffraction signal has a maximum on the qz-axis, indicating a preferential orientation of the membrane plane parallel to the surface of the hair. The keratin proteins in the cortex are known to organize in bundles whose structures are dominated by α-helical coiled-coils (Pauling & Corey, 1950; Pinto et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2014). 4, these signals were observed in the X-ray data in all specimen and assigned to the coiled-coil protein phase.
Bulge
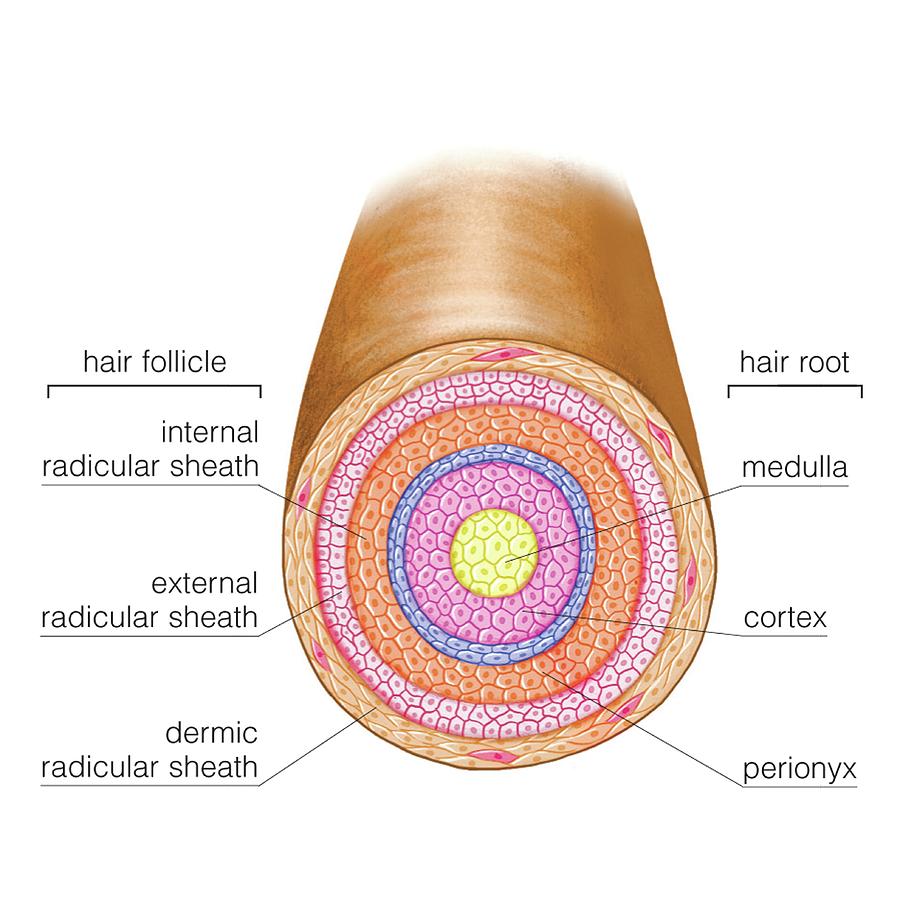
The adult human hair is around 20–180 µm in width, and generally grows to a length of approximately 90 cm. It consists of many layers including the cuticle, the cortex and the medulla. These layers are bound together by the cell membrane complex (Robbins, 2012).
Hair and Scalp Disorders
A period of 2-3 weeks is required for the transition to occur. At the level of the infundibulum, keratinization of the ORS changes to normal epidermal keratinization with formation of the granular cell layer and stratum corneum. The basal cell layer of the ORS contains inactive amelanotic melanocytes; in contrast, the surface epidermis that lines the infundibulum contains active pigmented melanocytes. The inactive melanocytes in the basal cell layer can become melanin-producing cells after skin injury (eg, chemical peels, laser resurfacing, dermabrasion). They proliferate and migrate toward the regenerating upper portion of the ORS and the epidermis. The outermost layer of the hair shaft (cuticle) consists of overlapping cells that are arranged like shingles.
Recent Activity
Hair follicles are structures within your skin that grow your hair. You’re born with millions of hair follicles in your skin. Damaged hair follicles lead to hair loss or reduced hair growth. Due to the large length scales involved, the signals from intermediate filaments occur at small scattering vectors, shown in Fig.
Glutamine Metabolism Controls Stem Cell Fate Reversibility and Long-Term Maintenance in the Hair Follicle - ScienceDirect.com
Glutamine Metabolism Controls Stem Cell Fate Reversibility and Long-Term Maintenance in the Hair Follicle.
Posted: Tue, 06 Oct 2020 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Some of your hairs might be growing, while others are falling out. The three features above were observed in all individuals in Fig. The underlying molecular structures will be quantitatively analyzed in the next section (Quantitative analysis of scattering results). We note that additional features are seen in some of the measurements in Fig.
Function
The outermost layer of the cuticle, the epicuticle, is a lipo-protein membrane that is estimated to be 10–14 nm thick (Swift & Smith, 2001). It is a long-standing question whether changes in the molecular structure of nail or hair can be related to certain diseases and potentially be used as a diagnostic tool. Such a technique would in particular be interesting and relevant as simple, non-invasive screening method for cancer (James et al., 1999; Briki et al., 1999; James, 2001). Abnormal kinky hair is, for instance, characteristic of giant axonal neuropathy (Berg, Rosenberg & Asbury, 1972). We previously reported that melatonin can be positively correlated with sheep litter size (48). However, the results of our analysis did not correlate with goat litter size.
How does hair grow?
De Novo Hair Follicle Morphogenesis and Hair Tumors in Mice Expressing a Truncated β-Catenin in Skin - ScienceDirect.com
De Novo Hair Follicle Morphogenesis and Hair Tumors in Mice Expressing a Truncated β-Catenin in Skin.
Posted: Thu, 14 Dec 2017 08:18:09 GMT [source]
We believe that this is because the purposes of the experiments were different and the treatments of embedded melatonin were different. Goats embedded with melatonin produced more cashmere if it was embedded for 6 months at 2 mg/kg every 2 months (18, 28). Sheep were generally embedded with melatonin 35 days to obtain more lambs (48). The rest of the hair is anchored in the follicle and it lies below the surface of the skin. The hair root is enveloped by the hair follicle which is a skin appendage that lies deep in the dermis of the skin.
Hair follicles originate in the first and second layers of your skin (epidermis and dermis). Follicles holding your terminal hair, or the hair that grows on your scalp, eyelashes and eyebrows, extend into the first and second layer of your skin and sometimes into the third layer (subcutaneous tissue). 1 between about 1.34 Å-1 and 1.63 Å-1, which are observed in some hair samples, agree with structural features reported in lipid membranes of different composition. The corresponding acyl chain correlation peaks were observed at Q values of ∼ 1.65 Å−1. Human scalp hair is a bio-synthesized material that has a complex internal structure.
It contains large melanocytes that supply melanin, or pigment, to the keratinizing cells of the hair matrix, thus determining hair color. Cells in the dermal papilla divide and differentiate, giving rise to the cortex, medulla, and cuticle of the hair. Peripheral cells in the bulb contribute to the internal and external root sheaths of the hair follicle. The molecular structure of the hair samples was studied using high-resolution X-ray diffraction, which covers length scales from molecules up to the organization of secondary structures. Despite the relatively small number of individuals (12) included in this study, some conclusions can be drawn. Genetics seem to play a role in this composition as identical patterns were observed in hair from father and daughter and identical twins, however, not for fraternal twins.
This layer is continuous with the epidermal basement membrane and is similarly periodic-acid-Schiff (PAS) positive and diastase resistant. Unlike the epidermal basement membrane, the glossy layer is much thicker and is visible with routine stains. During the catagen phase, the vitreous layer becomes much thicker and corrugated, which is a distinguishing feature of catagen phase hairs. Similar to the skin, hair gets its color from the pigment melanin, produced by melanocytes in the hair papilla. Different hair color results from differences in the type of melanin, which is genetically determined.
Hair follicles and their keratinized product, hair, are skin appendages present on nearly every part of the body. Areas of the body typically devoid of hair include the palmar and plantar surfaces, lips, and urogenital orifices. Sex hormones influence the distribution, texture, and color of hair. Hair follicles generate hair and help to provide epithelial stem cells used for wound repair.
This consecutive signaling process finally leads to the production of the mature follicle. The bulb of the hair extends to the arrector pili muscle at the follicular bulge. Between the arrector pili muscle and the entry site of the duct from the sebaceous gland is the isthmus, that leads to the pilary canal, or infundibulum. The pilary canal holds the hair and also forms the route for the discharge of sebum secreted by the sebaceous glands.

No comments:
Post a Comment