Table Of Content
If you accidentally pull out a strand of your hair and it has a ball (bulb) on the end of it, you didn’t pull out the follicle, and instead, you removed your hair root. If you notice you’re not growing hair in an area that you used to grow hair, talk to your healthcare provider. The size of each hair follicle in your body is different based on the size of the cells that make up the base of the structure. Hair follicles are microscopic and you can’t see them simply by looking at your skin. The cells in your hair follicles help your body heal after a wound. When your body receives an injury, the cells within your hair follicles are closest to the wound and quickly move to the site of the wound to start the healing process.
How It Gets Its Shape
Besides the cosmetic concerns of hair color, growth, and distribution, hair plays a vital role in thermoregulation, tactile sensation, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation protection. Diseases of hair follicles and hair are an important concern to the general population and have been an active topic of research in recent years. Melatonin promotes hair follicle growth in humans (12) and goats.
2. Structure of the hair
Each hair grows for around 3 to 5 years before undergoing a resting phase of several months, and then, eventually, it falls out. Whether it is straight, curly, or wavy, your hair is unique to you. Curvy or straight hair follicles set the look of each hair throughout your life. The most important function of hair in mammals is that of insulating against cold by conserving body heat. The differing colours and colour patterns in hair coats can also serve purposes of camouflage and of sexual recognition and attraction among the members of a species.
What is the function of a hair follicle?
The mouse EDAR mRNA is expressed in the epithelium before placode formation, and then becomes restricted to placodes, whereas the EDA mRNA is still expressed even after placode formation [3, 6, 8]. In the placode stage, activated WNT and EDAR control the localized accumulation of sonic hedgehog (SHH), which is essential for the downgrowth of the hair germ [2]. In contrast to EDA and EDAR, members of the bone morphogenic protein (BMP) family of secreted signaling molecules seem to be inhibitors of placode formation. The antagonist named Noggin neutralizes BMP activity via regulation of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 (LEF1) expression [4].
It’s possible that a damaged follicle will stop producing hair. Certain conditions, such as alopecia, can cause follicles to stop producing hair altogether. The hair samples gathered were cut into strands around 3 cm long. Care was taken to not stretch or deform the hair strands during this process. For each subject, around 10 strands were taped onto a flexible cardboard apparatus as shown in Fig.
Keratinocytes of the Upper Epidermis and Isthmus of Hair Follicles Express Hemoglobin mRNA and Protein - ScienceDirect.com
Keratinocytes of the Upper Epidermis and Isthmus of Hair Follicles Express Hemoglobin mRNA and Protein.
Posted: Fri, 17 Nov 2023 11:41:59 GMT [source]
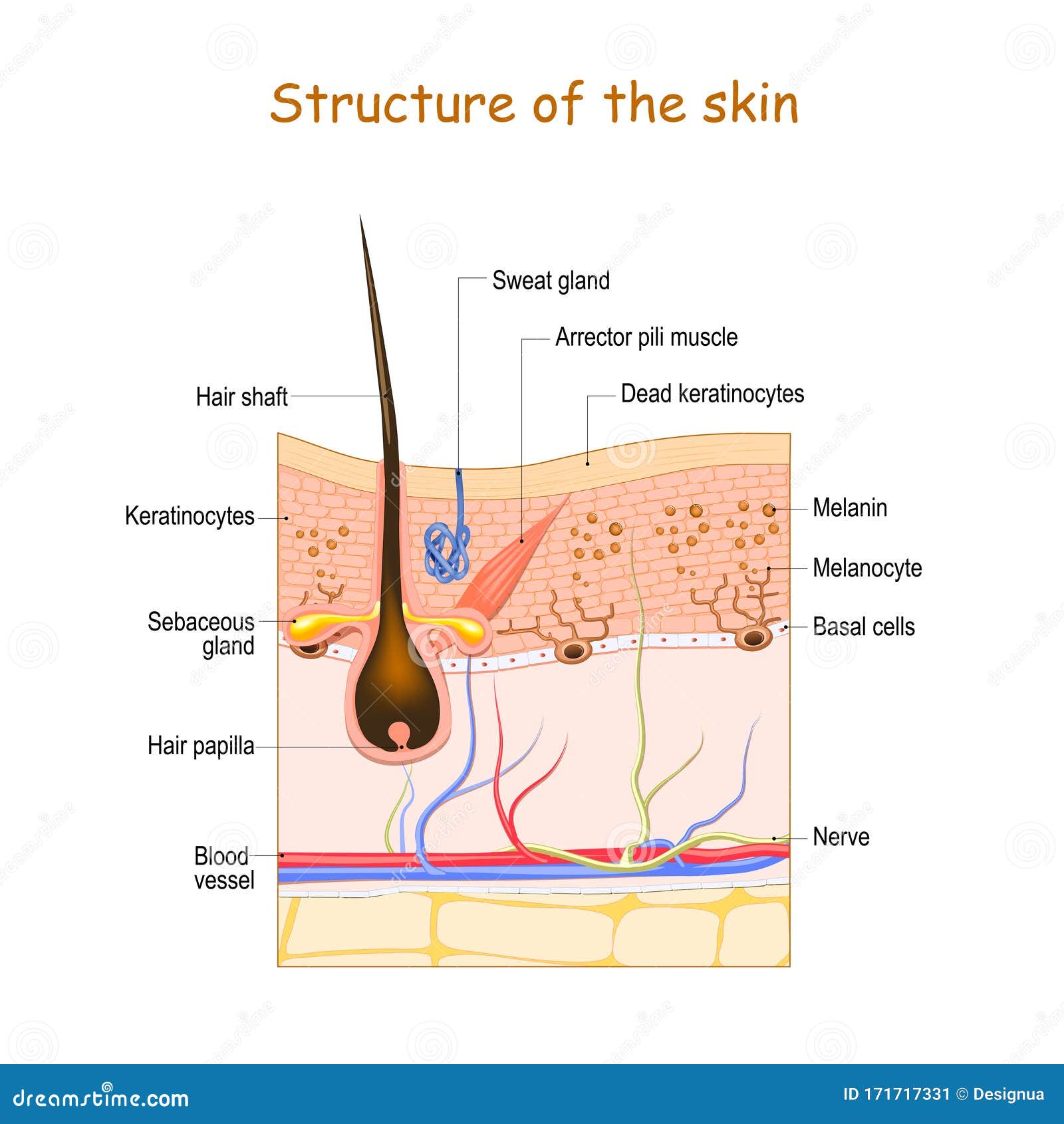
Subtle hair loss on the lower extremities can sometimes hint at the underlying peripheral arterial disease. Although vellus hairs greatly outnumber terminal hairs, the latter are more important. Therefore, the discussion of hair anatomy in this article focuses on terminal hairs. The bulge also provides the insertion point for the arrector pili—a tiny band of muscle tissue. The contraction of these muscles is what causes hairs to stand on end when you get goosebumps. The hair bulb also contains cells called melanocytes that produce various kinds of melanin pigments.
Study selection and characteristics
Alopecia can sometimes lead to alopecia universalis - total hair loss from all over the body. The average human has 100,000 hair follicles on the skin. Thus, your hair follicles deserve some spotlight when it comes to hair care. So, keep reading to understand the structure of your hair follicles, its functions and hair issues.
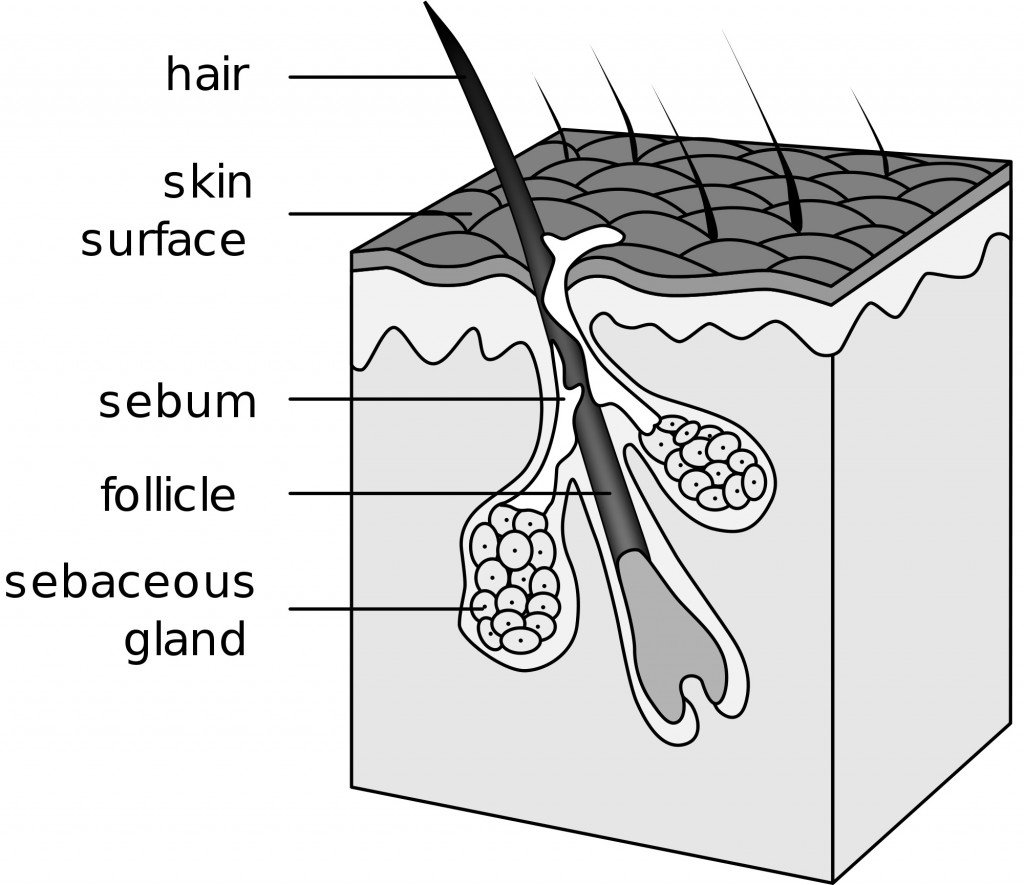
Hair is a keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis. Strands of hair originate in an epidermal penetration of the dermis called the hair follicle. The hair shaft is the part of the hair not anchored to the follicle, and much of this is exposed at the skin’s surface.
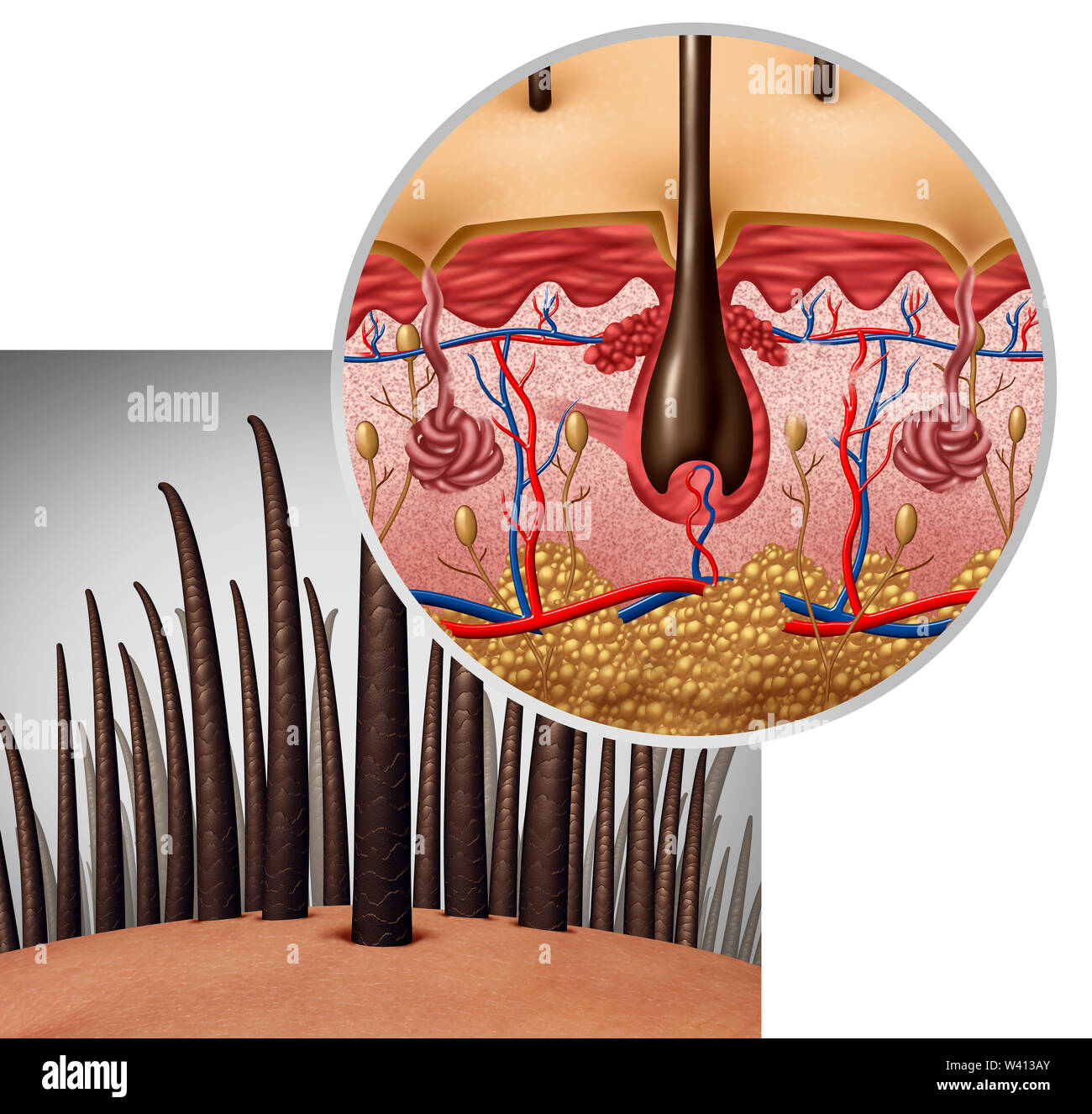
Microanatomy of Catagen Phase Hair
Goat melatonin receptor 1A SNPs affect melatonin to exert its function. The wild-type gene defect of MR1 is a valuable animal model. Future studies should focus on the relationship between goat SNPs and the effect of embedded melatonin. This study can provide a reference for improving cashmere production and a suggestion for animal models of human alopecia. Figure 5 Effect of melatonin on hair follicle growth in humans and goats.
This segment includes the bulb, which contains the follicular matrix surrounding the sides and top of the dermal papilla. The papilla interacts with the matrix, which has the highest mitotic rate of any organ. The matrix is the part of the hair follicle where matrix keratinocytes proliferate to form the hair shaft of growing hair.
If the fitted intensity cannot conform to the shape of the data intensity, more peaks will be added in the following runs until a good fit is acquired. This process was repeated for all 12 subjects and performed with little or no consultation of previous fittings to minimize bias. The cuticle is the outermost layer formed by flat overlapping cells in a scale-like formation (Robbins, 2012). These cells are approximately 0.5 µm thick, 45–60 µm long and found at 6–7 µm intervals (Robbins, 2012).
Rats (3), mice (4), guinea pigs (5), rabbits (6), and dogs (7) are animal models for studying human hair follicles. Comparative studies on the impact of diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) on mouse and dog alopecia suggest that mice may be an especially sensitive species (41). In a healthy human, 90% of your hair follicles are in the growth phase or anagen phase. During this resting phase, the hair follicle changes in structure, essentially shriveling up in the skin. To start a new cycle of hair growth, the follicle grows back to its original shape.
Women will typically present with a widening part and thinning at the top of the scalp. A genetic predisposition to increased hair follicle sensitivity to circulating androgens causes this type of hair loss. The bulb is the rounded structure deep in the skin at the root of the hair that surrounds the papilla and germinal matrix. It has several types of stem cells, which develop into specialized cells and can renew themselves over a long period of time.

No comments:
Post a Comment